CDC Setup
This guide provide specific details on working at CDC.
Cygwin Setup in Windows
Cygwin Installation does not require elevated or admin privilege to install.
- Download Cygwin Setup executable.
- Open up Powershell.
- Navigate to the executable folder (usually c:\users\-username-\downloads)
- Run
setup-x86_64.exe --no-adminto run cygwin. - Install from a trusted source in the US. ex. Rochester Institute of Technology (RIT), or Virginia Tech (VT).
- Install the following set of tools, the most important one being openssh.
autossh
bash-complete
bind-utils
corkscrew
cron
curl
dnsperf
git
iperf
nano
ncftp
netcat
openssh
ping
rsync
socat2
stunnel
unzip
whois
- Open the cygwin terminal, and configure bashrc so that git branches appear in your terminal if you end up using it for git.
- Add this to the bottom of ~/.bashrc
parse_git_branch() {
git branch 2> /dev/null | sed -e '/^[^*]/d' -e 's/* \(.*\)/ (\1)/'
}
PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\[\033[01;32m\]\u@\h\[\033[00m\]:\[\033[01;34m\]\w\[\033[00m\]\[\033[33m\]$(parse_git_branch)\[\033[00m\]\$ '
- When using cygwin as a SSH client, the SSH configurations are stored in the ~/.ssh/ folder. You can generate keys following the SSH client guide.
Root Signing Certificate
Internal websites uses particular root signing certificates, which are public keys that appears on SSL/TLS certificates on internal cdc.gov domains as they are signed by these root certificate authority. In addition, different network connection paths may cross a man-in-the-middle firewall where the firewalls will reissue a new SSL/TLS certificate using these root certificate authorities. The client you are using (ex. browsers, curl, python/nodejs application) will need to trust these root certificates or ignore HTTPS warnings to establish a SSL/TLS connection.
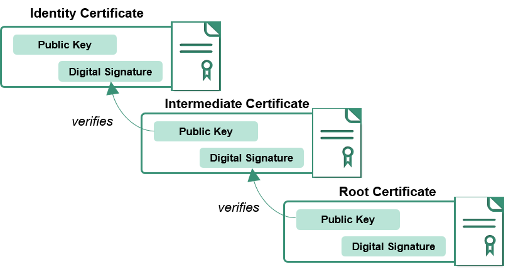
Within CDC network, these are generally the root certificate files that are presented by internally hosted webservers and firewalls. There is a bundle-ca.pem file including all of the certificates.
| Root Certificate | Format | Type | Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|
| CDC-G2-S1.pem | PEM | Intermediate | March 14 2028 4:46:42 PM EDT |
| CDC-G2-PA.pem | PEM | Intermediate | May 06 2029 9:55:14 AM EDT |
| CDC-G2-ZSH.pem | PEM | Intermediate | May 05 2029 1:13:45 PM EDT |
| CDC-G2.pem | PEM | Root | March 09 2033 2:53:39 PM EDT |
| bundle-ca.pem | PEM | N/A | N/A |
Instructions For Browsers
- Download bundle-ca.pem.
- Open up browser settings (ex. Firefox) and type in "cert" and import these certificates into the browser's truststore.
- Visit https://intranet.cdc.gov with the proxy turned on to see it go through.
Instructions for Operating System
This is an optional step. Sometimes clients trust the operating system truststore, other times, they have their own so it may be necessary to go through various truststores for all the client (ex. NodeJS, python) to get through HTTPS errors.
- Download bundle-ca.pem.
- Follow the step below to copy the certificate to the local ca-certificate location.
- Update the truststore.
sudo cp bundle-ca.pem /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/bundle-ca.crt
sudo update-ca-certificates
FoxyProxy
FoxyProxy is optional, but can ease the setup considerably by shortening context switches between personal and official use.
- Use and import the Firefox FoxyProxy settings for intranet browsing.
- Use and import the Chrome FoxyProxy settings for O365 Usage for Office 365 (O365) such as Teams, Sharepoint, and Outlook usage. To generate this file in Chrome, open up the Chrome extension settings for FoxyProxy, open dev tools (ctrl+shift+i), open the Console tab, and run
console.log((new XMLSerializer).serializeToString(generateXMLFromStorage()))and copy the XML block into a .fpr file.